
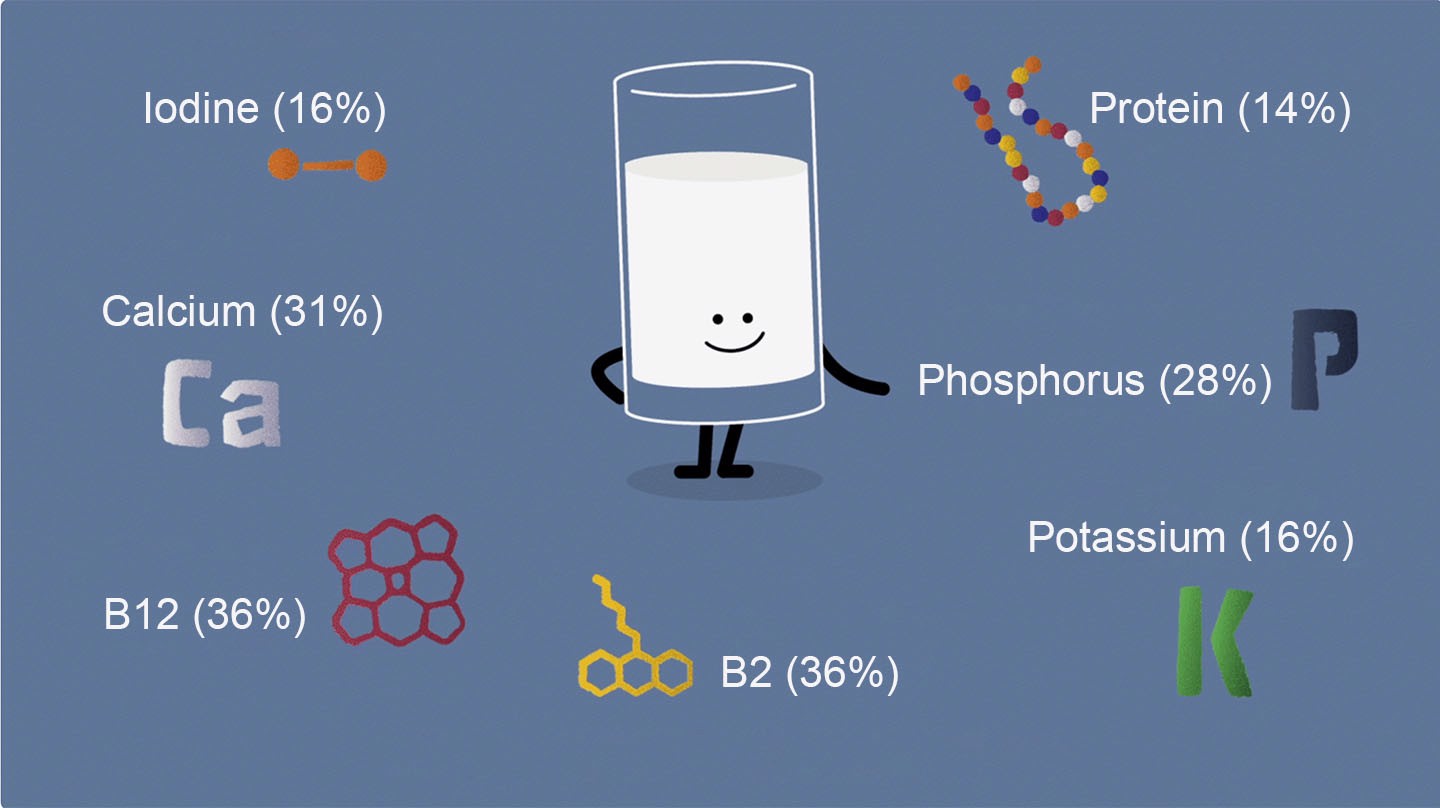
Milk contains protein, calcium, vitamin B2, vitamin B12, phosphorus, iodine and potassium. Here’s how the nutrients in milk benefit your body.
Nutrients like calcium, that helps develop your bones as you grow up and maintain them throughout life, and protein that help you maintain a normal muscle function, are part of the natural milk nutrition package. Drinking milk or eating yoghurt is a very easy way to get milk nutrition on a daily basis, and milk is recommended by many dietary guidelines across the world.
Let’s take a look at milk nutrition and how the individual nutrients in milk benefit your body. But before we start, please note that the specific recommendations on daily intake on this website are following the recommendations in Denmark, where Arla is legally based. Recommendation vary slightly in other countries and you should always seek detailed advise from your own national health authorities.
Calories in milk
Are there a lot of calories in milk? And is milk fattening? We know that some people, especially teenagers may stop drinking milk because they are afraid to gain weight or want to lose some kilos.
Skimmed milk or skim milk is lowest in calories, while whole milk is highest in calories, and in between the two is semi-skimmed milk.
The level of calories depend on the amount of fat in your preferred milk as milk types and fat levels vary from country to country. The easiest way to find the exact answer to how many calories are in your milk is to go to the product label on the packaging and look for Kcal.
But this overview might give you an indication of which milk has the most fat and how many calories per 100 ml are in the different milk types:

Many national dietary guidelines recommend that you choose low-fat milk in your daily diet. In a healthy and balanced diet, there is room for a little whole milk to add a more creamy taste and texture to your cooking, your latte or cup of tea.
The amount of calcium, protein, vitamin B2 and vitamin B12, iodine, phosphorus and potassium is the same in skimmed milk, semi-skimmed milk and whole milk.
On the label, you can also check out the actual amount of calories versus nutrients in milk and compare the result to other foods in your diet. You might find that milk is less fattening and more nutrient-rich than you expected. For example, milk is a source of calcium and calcium is needed to maintain normal growth and development of bones and teeth throughout life.
Milk is also rich in protein, and protein helps you maintain normal muscle mass and growth of muscles mass when you exercise. If you take away milk from your diet, you should consider if you are getting the recommended daily intake of calcium and protein from other food sources.
Is protein in milk good for your muscles?
Protein is the main building block of your muscles and milk is a source of protein and also potassium that contributes to a normal muscle function.
Apart from raw eggs, milk provides the only liquid protein that you can find in nature. Just one glass of milk (200ml) provides an adult person with enough milk protein to cover 14% of the total needed daily intake of protein.
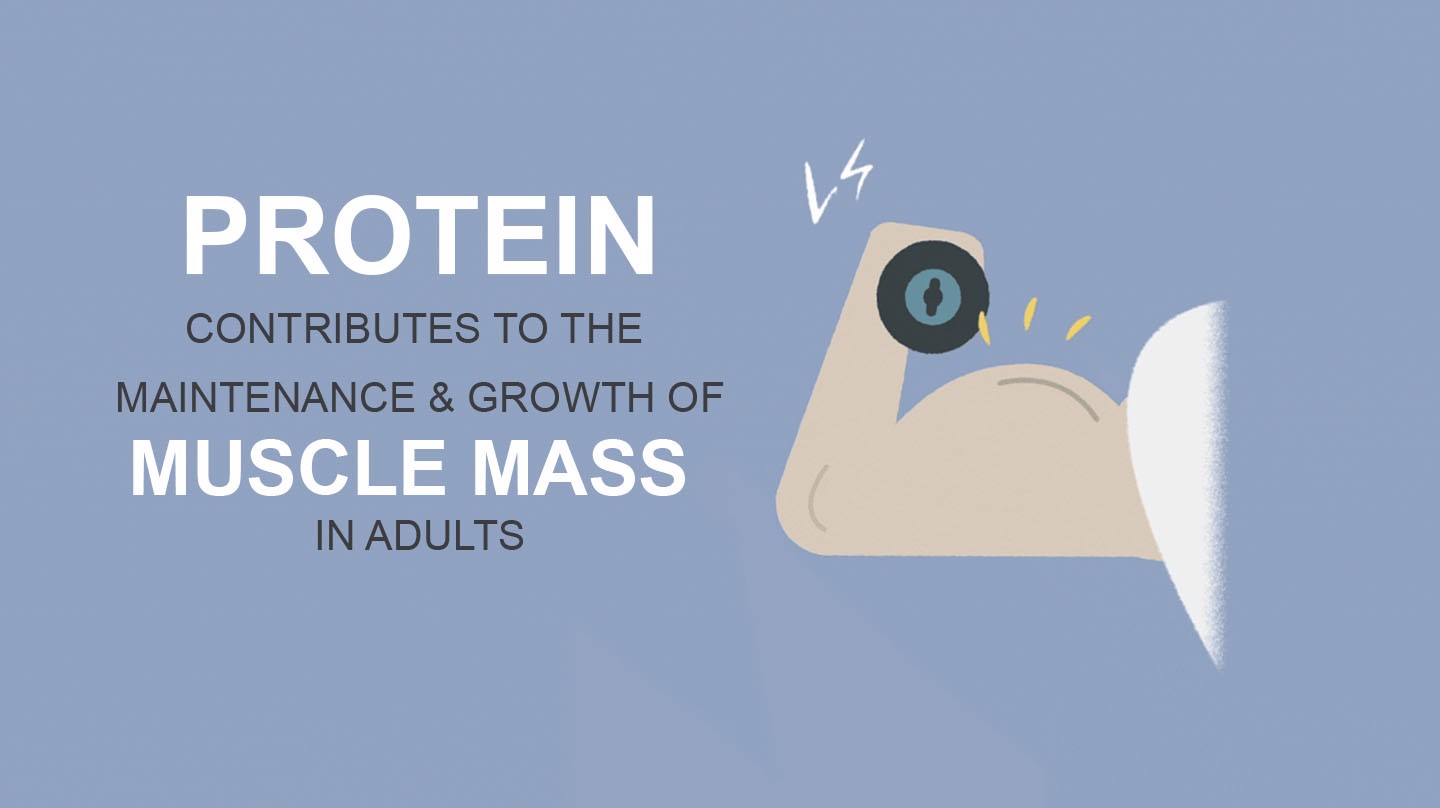
15-20% of your body is protein, which equals to 12kg for a person of who weighs 70kg. Getting an adequate amount of protein helps you maintain your muscle mass and grow your muscle mass when you exercise.
As an adult, protein also helps you maintain normal bones throughout life. Protein is also necessary for kids as protein is needed for normal growth and development of children’s bones.

There are two main types of protein in milk - casein and whey protein. Milk, yogurt and cottage cheese are rich in milk protein. Cheeses such as hard or semi-hard yellow cheese and white cheese are also rich in milk protein, but are also often high in fat. Other sources of protein are meat, eggs, fish, poultry, legumes (for example chickpeas, beans and lentils), soy products such as tofu and certain types of bread and cereals.
If you eat a healthy and balanced diet that cover many of these food categories, you will get your proteins from both vegetable and animal sources.
Is calcium in milk good for your bones?
Do you really need milk to maintain healthy bones? Is calcium in milk good for your teeth? Well, it’s a fact that the level of calcium in milk is high, and calcium helps you to maintain normal bones and teeth throughout life. Calcium is also good for kids as calcium helps grow and develop children’s bones. Our bones mainly consists of calcium and are continuously being rebuilt throughout life.

Getting calcium from milk or eating yogurt or hard yellow cheeses is an easy way to get calcium every day.
Just one glass of milk or a bowl of yogurt (200 ml) provides you with 31% of the total needed daily intake of calcium for an adult. If you drink one glass of skyr drink (200 ml) or eat 2 slices of low-fat yellow cheese (55 g) you will get 400 mg of calcium, half of the daily recommended amount.
Milk vitamins and other nutrients in milk
Vitamin B2 in milk
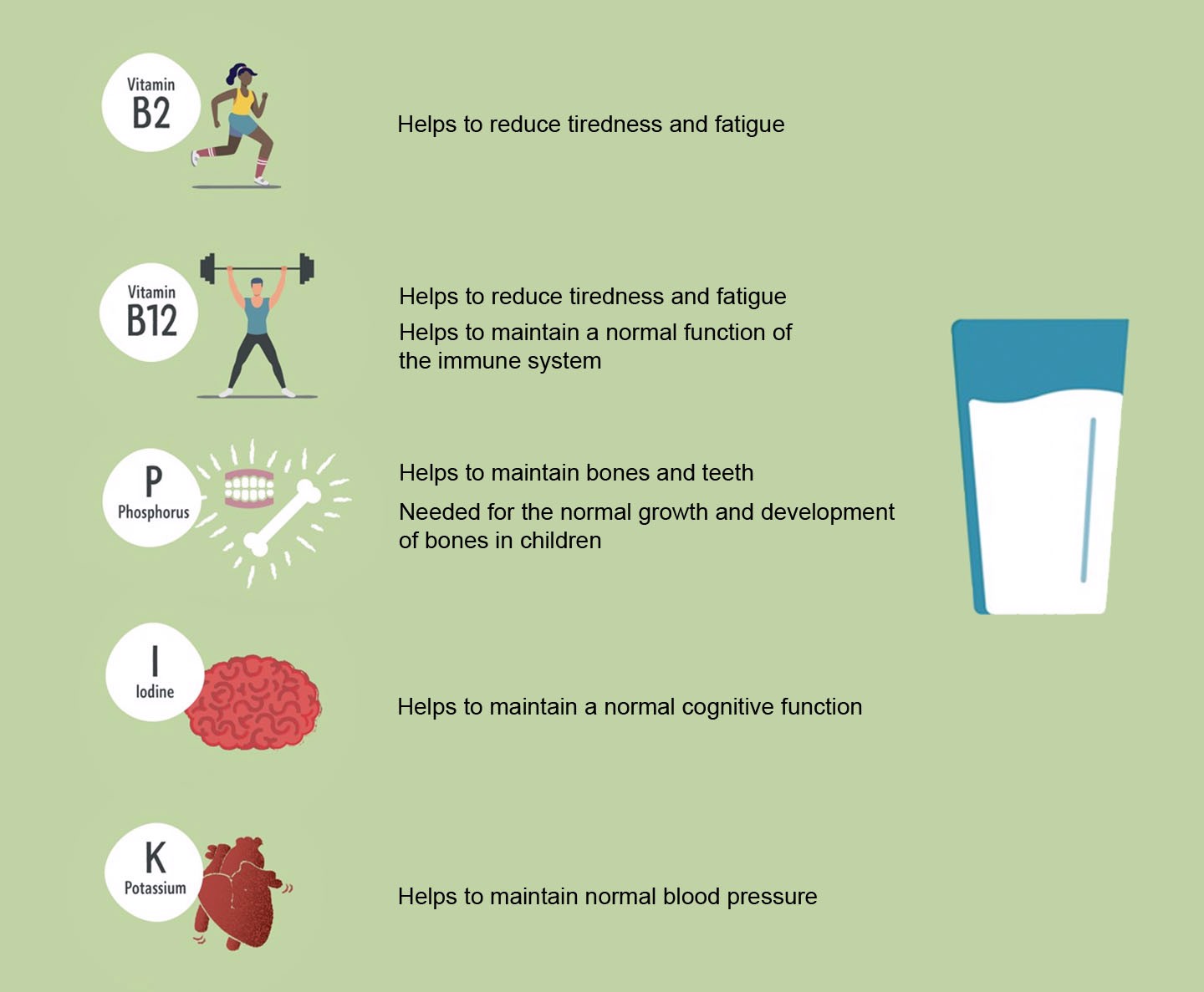
Vitamin B2, also called riboflavin contributes to reduce tiredness and fatigue. Milk contains vitamin B2 and just one glass of milk (200 ml) provides you with 26% of the needed daily intake of vitamin B2.
Vitamin B12 in milk
Vitamin B12 contributes to reducing tiredness and fatigue and helps maintain a normal function of the immune system. Milk contains vitamin B12 and just one glass of milk (200 ml) provides you with 36% of the needed daily intake of vitamin B12.
Phosphorus in milk
Milk contains phosphorus, iodine and potassium. Phosphorus helps you maintain bones and teeth and is also needed for the normal growth and development of bone in children. Just one glass of milk (200 ml) provides you with 28% of the needed daily intake of phosphorus.
Iodine in milk
Iodine helps you maintain a normal cognitive function. Just one glass of milk (200 ml) provides you with 16% of the needed daily intake of iodine.
Potassium in milk
Potassium helps you maintain of normal blood pressure. Just one glass of milk (200 ml) provides you with 16% of the needed daily intake of potassium.
Is there sugar in milk?
The calories in milk are not only decided by the level of fat but also the sugar level. Plain milk does not contain added sugars. Milk has a natural content of milk sugar, also called lactose, of 4,7g of per 100g. In plain yogurts the amount of natural lactose is 3,7g.
Lactose provides the slightly sweet taste that is naturally present in plain milk. Added sugar in dairy is mostly found in flavoured yogurts and yogurt drinks and flavoured milk-based beverages.
Sugar or carbohydrates are naturally present in many types of foods, but also added to many products to give them the sweet taste that many of us like. However, too much sugar is bad for you, which is why many national dietary guidelines recommend that you reduce your intake of sugars.
Does lactose-free milk have the same nutrients as regular milk?
Almost! The amount of nutrients are slightly reduced during the process of taking out the lactose from the milk. But lactose-free milk is still considered to be rich in for example calcium and protein.
Know more about lactose free products .

