
There's no need to avoid dairy if you are lactose intolerant. In lactose free products, we have split the lactose into smaller molecules that you can digest. Here's how.
If you are lactose intolerant, you might enjoy lactose free milk that is produced in a special way to help you digest dairy without stomach pains.
Firstly, a short explanation of what causes lactose intolerance.
Lactose is a sugar molecule that is naturally present in milk. For you to digest lactose, you need an enzyme in your body called lactase, which can split lactose into two smaller molecules: glucose and galactose. The smaller molecules can then individually be absorbed in the small intestine with no discomfort.
If you have low levels of lactase, the split of the lactose molecule doesn’t take place before it hits the large intestine, where gut bacteria will start to break it down. As side effect of the bacteria’s process, some people get unpleasant symptoms such as stomach pain or bloating.
Read more about the symptoms of lactose intolerance
Some people with lactose intolerance can consume more dairy before experiencing symptoms while others can consume very little. Sometimes it’s a permanent condition, sometimes it’s only temporary.

How does lactose free dairy work?
Arla follows a gentle process to make the milk lactose free while ensuring that the nutrients naturally present in milk are preserved.
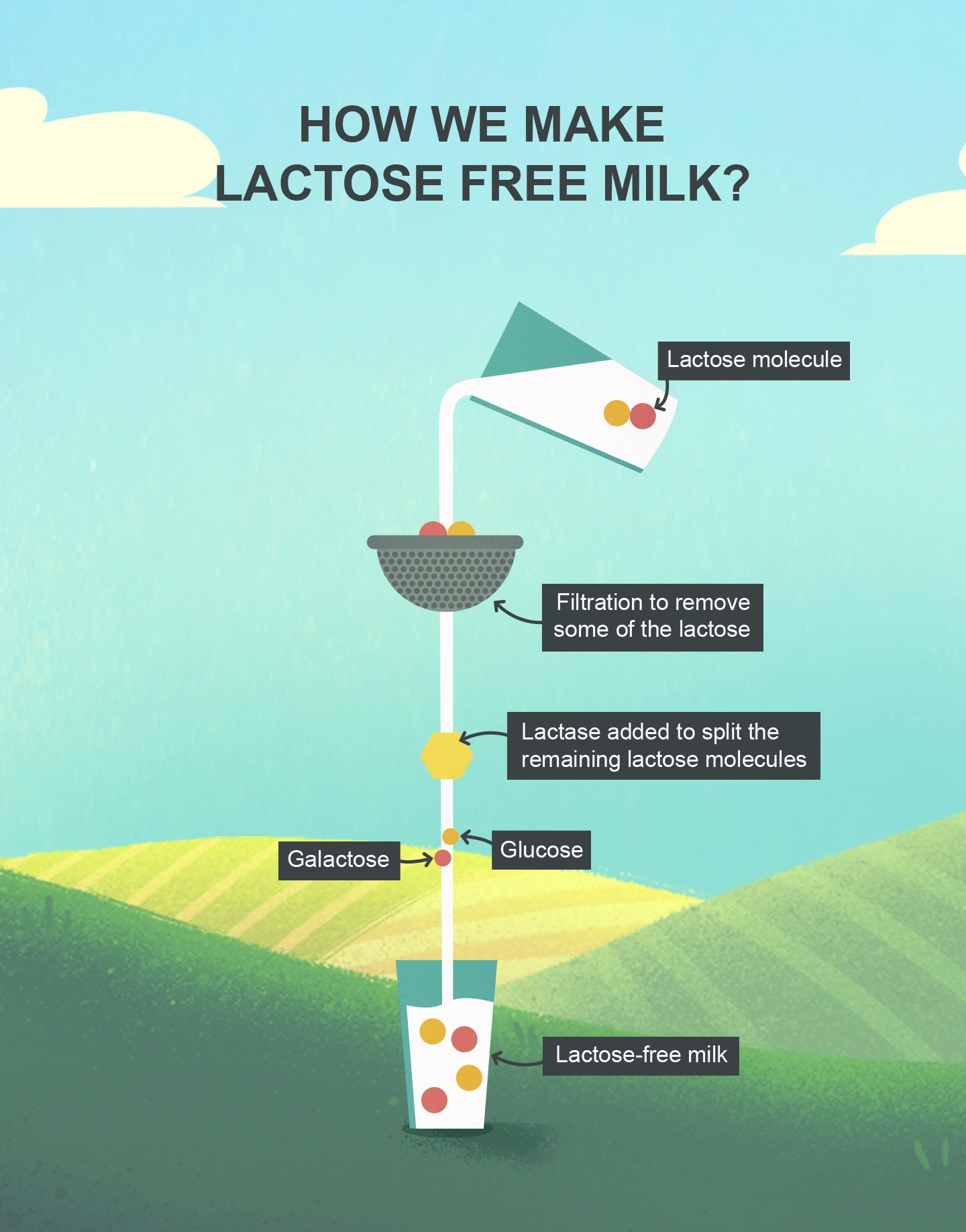
The process consists of two steps. First the milk is passed through filters that remove 40% of the lactose, while preserving calcium and other nutrients that exist naturally in the milk. In the following step, lactase is added. Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose to the simple sugars glucose and galactose. Lactase is produced naturally by some, but not all, people. It is usually insufficient produced in lactose intolerant people.
This gentle manufacturing process means that the calcium in the milk is preserved throughout the process, thus eliminating the need to add extra calcium to the milk afterwards.
As part of the lactose is filtered out in the process, there are fewer carbohydrates in the lactose free milk, which makes the calorie content a bit lower compared to regular milk.
Lactose free or low lactose?
A lactose free milk is completely lactose free. However there is also milk that is low in lactose content. This milk contains less than 1g of lactose per 100g. Low lactose milk is produced exclusively by adding lactase, which is the substance that breaks down lactose as mentioned above. When lactose is broken down, it gives the milk a sweeter taste. Arla’s lactose free milk on the other hand is filtered first, so less lactase is added, making it taste much like regular milk, and not as sweet as low lactose milk.
Lactose free milk is suitable for everyone who is lactose intolerant, as well as anyone who opts out of regular milk for other reasons. Lactose free milk can be consumed similar to regular milk. It can also be used in cooking such as in rice pudding.
As the process to produce lactose free milk is more advanced, this makes lactose free milk slightly more expensive than regular milk.
In lactose free products, we have split the lactose into glucose and galactose for you. At most dairies we use technologies to first pass the milk through filters that remove 40% of the lactose. Next, we remove the remaining lactose by adding the enzyme lactase that can separate the two molecules.
Lactose is a sugar molecule, and as a consequence of the filtering process, the level of carbohydrates is slightly reduced. The level of for example calcium and protein is roughly the same.
If you’re wondering how much lactose you can tolerate, there is no clear-cut answer. This differs from one person to the other. It is quite an individual experience how much lactose you can tolerate and how you react if you are lactose intolerant. Consuming too much lactose at once by lactose intolerant people can cause bloating, stomach rumbling and diarrhoea. It is best to visit your doctor to get this checked and eventually find out the amount that works for you.
Lactose intolerant people can typically consume yellow cheese as it’s naturally low in lactose - under 0.05g of lactose per 100g of cheese. This is because the lactic acid bacteria break down the lactose in the fermentation process. Similarly, some lactose intolerant people may be able to tolerate yogurt, as lactic acid bacteria in the yogurt ease the digestions of lactose due to fermentation.
Organic lactose free milk
In some countries, Arla offers organic lactose free milk. The organic lactose free milk is made the same way as standard lactose free milk, only based on organic milk from organic farms that comply fully with controlled organic standards
Learn more about Arla Lactose Free Milk


